Recursos-Internet
Internet courses resources
Tuesday, October 1, 2019
1-An internet resource are those that have access to texts, images, videos, software and antivirus. It also gives you the option of entering emails to gain access to other computers or technological devices.
2-Are those applications that give you access to a variety of functions such as being able to enter different technology devices and other types of applications
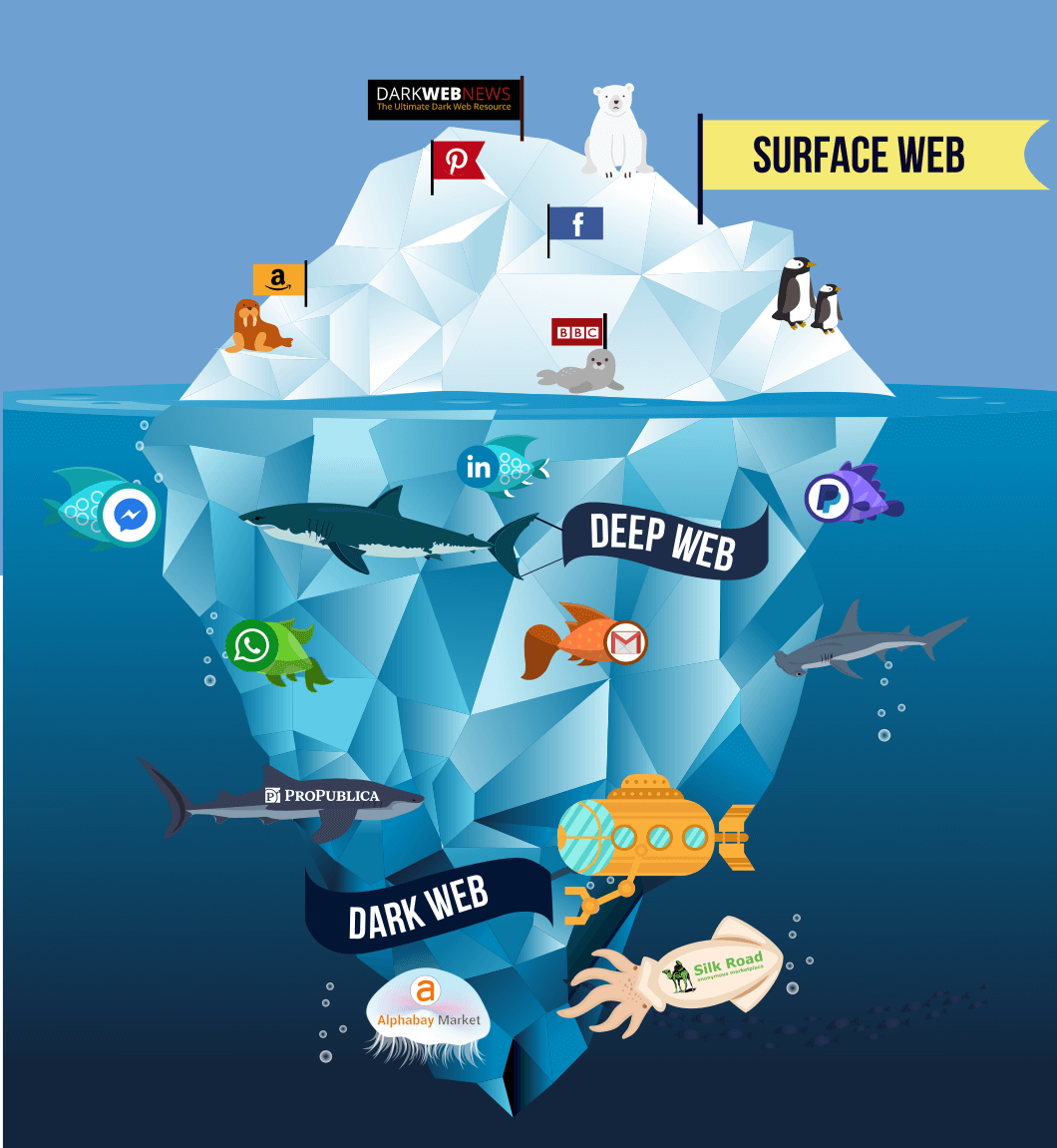
-DEEP WEB-
(Deep Internet, invisible Internet, hidden Internet)
It is the internet content that is not indexed by conventional search engines, due to various factors.The term is attributed to the computer scientist Mike Bergman.It is the opposite of the superficial Internet.
The main cause of the existence of the deep internet is the inability of search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc.) to find or index much of the information on the Internet. If the search engines had the ability to access all the information then the magnitude of the "deep internet" would be reduced almost entirely. However, even if the search engines could index the information on the deep internet, this would not mean that it ceased to exist, since private pages will always exist. Search engines cannot access the information on these pages and only certain users, those with passwords or special codes, can do so.
In the Deep Web you can establish contacts that are not monitored, nobody is there watching. In addition, both merchandise and payment transfers are virtually impossible to track. The web is divided into two parts, the superficial web and the deep web. The latter is known as Deep Web, where all content that is not indexable by search engines is located, or that users cannot access through a web browser such as DuckDuckGo, Startpage, Yandex, Ecosia, Yahoo !, Google or Bing
The deep internet is not a forbidden or mystical region of the internet, and technology related to it is generally not conspiratorial, dangerous or illegal. It houses all kinds of resources that are difficult to access through common methods such as popular search engines.
A part of the deep internet consists of internal networks of scientific and academic institutions that form the so-called Invisible Academic Web: ("Invisible academic Internet") which refers to databases that contain technological advances, scientific publications, and academic material in general, which cannot be easily accessed.
Tuesday, October 1, 2019
1-An internet resource are those that have access to texts, images, videos, software and antivirus. It also gives you the option of entering emails to gain access to other computers or technological devices.
2-Are those applications that give you access to a variety of functions such as being able to enter different technology devices and other types of applications
-DEEP WEB-
(Deep Internet, invisible Internet, hidden Internet)
It is the internet content that is not indexed by conventional search engines, due to various factors.The term is attributed to the computer scientist Mike Bergman.It is the opposite of the superficial Internet.
The main cause of the existence of the deep internet is the inability of search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc.) to find or index much of the information on the Internet. If the search engines had the ability to access all the information then the magnitude of the "deep internet" would be reduced almost entirely. However, even if the search engines could index the information on the deep internet, this would not mean that it ceased to exist, since private pages will always exist. Search engines cannot access the information on these pages and only certain users, those with passwords or special codes, can do so.
In the Deep Web you can establish contacts that are not monitored, nobody is there watching. In addition, both merchandise and payment transfers are virtually impossible to track. The web is divided into two parts, the superficial web and the deep web. The latter is known as Deep Web, where all content that is not indexable by search engines is located, or that users cannot access through a web browser such as DuckDuckGo, Startpage, Yandex, Ecosia, Yahoo !, Google or Bing
The deep internet is not a forbidden or mystical region of the internet, and technology related to it is generally not conspiratorial, dangerous or illegal. It houses all kinds of resources that are difficult to access through common methods such as popular search engines.
A part of the deep internet consists of internal networks of scientific and academic institutions that form the so-called Invisible Academic Web: ("Invisible academic Internet") which refers to databases that contain technological advances, scientific publications, and academic material in general, which cannot be easily accessed.
Digital divide
Digital divide is understood as the distance in access, use and appropriation of technologies both geographically, socioeconomically and also in gender dimensions, in articulation with other cultural inequalities, etc. It should be noted that the digital divide is related to the quality of the technological infrastructure, the devices and connections, the ignorance of the use of the tool, but above all, with the cultural capital to transform the circulating information into relevant knowledge.1
The Digital divide according to Serrano and Martínez (2003, cited by the OEI (2014) is defined as: the separation that exists between people (communities, states, countries ...) that use Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) ) as a routine part of their daily lives and those who do not have access to them and who, although they do not know how to use them. "According to Eurostat, the digital divide refers to the" distinction between those who have access to Internet and can make use of the new services offered by the World Wide Web, and those that are excluded from these services "
Digital divide is understood as the distance in access, use and appropriation of technologies both geographically, socioeconomically and also in gender dimensions, in articulation with other cultural inequalities, etc. It should be noted that the digital divide is related to the quality of the technological infrastructure, the devices and connections, the ignorance of the use of the tool, but above all, with the cultural capital to transform the circulating information into relevant knowledge.1
The Digital divide according to Serrano and Martínez (2003, cited by the OEI (2014) is defined as: the separation that exists between people (communities, states, countries ...) that use Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) ) as a routine part of their daily lives and those who do not have access to them and who, although they do not know how to use them. "According to Eurostat, the digital divide refers to the" distinction between those who have access to Internet and can make use of the new services offered by the World Wide Web, and those that are excluded from these services "
Hierarchy of Internet resource management
IANA; Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (whose acronym is IANA) is the entity that oversees the global assignment of IP addresses, stand-alone systems, root servers of DNS domain names and other resources related to Internet protocols. It is currently a department operated by ICANN.
Initially, IANA was administered primarily by Jon Postel at the Institute of Information Sciences (ISI) of the University of Southern California (USC), under a USC / ISI contract with the United States Department of Defense , until ICANN was created to assume responsibility under a contract of the Department of Commerce.
RIR; A Regional Internet Registry, in English Regional Internet Registry (RIR), is an organization that oversees the allocation and registration of Internet number resources within a particular region of the world. Resources include IP addresses (both IPv4 and IPv6) and autonomous system numbers (for use in BGP routing).
The global IP address registry was originally a list of IP addresses with details of the organization to which it had been assigned. Given the growth of this list, the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) emerged to regulate the assignment of IP addresses. With the rapid expansion of the Internet, IANA could not meet the demand for addresses, the idea of managing numerical resources through regional subsidiary organizations, establishing the Regional Internet Registries (RIR).
NIR: A National Internet Registry (NIR) mainly distributes Internet resources to its members or constituents, which are generally LIRs.
LIR: Local Internet Registration (LIR) is an IR that in turn allocates Internet resources to users of the network services it provides. LIRs are generally ISPs, whose clients are primarily end users and possibly other ISPs.
ISP: An Internet Service Provider primarily allocates IP address space to the end users of the network services it provides. Your customers may be other ISPs. ISPs do not have geographical restrictions as do NIRs.
EU: An end site is defined as an end user (subscriber) that has a business or legal relationship (same or associated entities) with an Internet service provider that involves:
to the service provider by assigning an address space to the end user.
to the service provider providing a transit service for the end user to other sites.
to the service provider transporting end user traffic.
to the service provider announcing an aggregate route prefix containing the range assigned by LACNIC to the end user.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario